



Next: Quadratische Näherung
Up: Gauß - Quadratur
Previous: Vorbemerkungen
Für 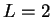 steht in (
steht in (![[*]](file:/mnt/bison/local/lib/latex2html/icons/crossref.gif) )
)
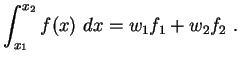 |
(4.32) |
Wir fordern, dass diese Formel für 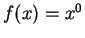 und
und 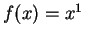 exakt
ist.
exakt
ist.
Also muss gelten:
Die Lösung des Gleichungssystems führt auf
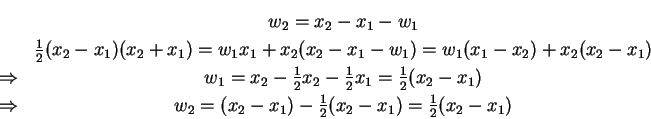 und somit
und somit
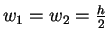
© R.Hilfer et al., ICA-1, Univ. Stuttgart
28.6.2002
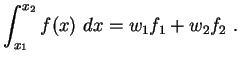
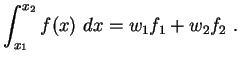
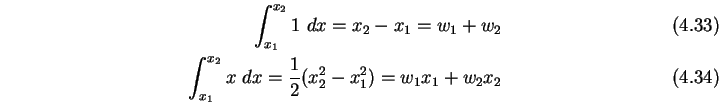
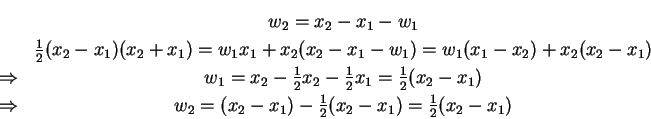 und somit
und somit