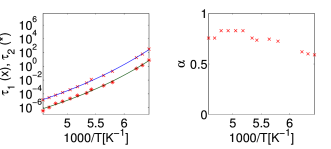
5 Temperature dependence of the parameters
[page 1287, §1]
[1287.1.1] Because the data have been fitted at different temperatures we are able
to observe the temperature dependence of the fitting parameters.
[1287.1.2] For ![]() and
and ![]() we perform Vogel-Tammann-Fulcher fits
provided by equation (13).
[1287.1.3] From the fits we obtain the Vogel-Fulcher temperatures
we perform Vogel-Tammann-Fulcher fits
provided by equation (13).
[1287.1.3] From the fits we obtain the Vogel-Fulcher temperatures ![]() and
and
![]() as well as the fragility parameters
as well as the fragility parameters ![]() and
and
![]() for the relaxation times
for the relaxation times ![]() and
and ![]() for model A and model B (see Table 2).
for model A and model B (see Table 2).
| material | model | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 5-methyl-2-hexanol | A | ||||||
| 5-methyl-2-hexanol | B | ||||||
| methyl-m-toluate | A | ||||||
| methyl-m-toluate | B | ||||||
| glycerol | A | ||||||
| glycerol | B |
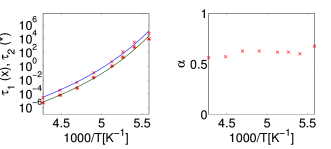
[1287.2.1] For all fits we see a temperature dependence of the
relaxation times ![]() and
and
![]() (Fig. 4 - Fig. 6)
that follows the Vogel-Tammann-Fulcher fitting function remarkably well.
[1287.2.2] The relaxation times also show a clear downward trend as the
temperature increases, which confirms that
(Fig. 4 - Fig. 6)
that follows the Vogel-Tammann-Fulcher fitting function remarkably well.
[1287.2.2] The relaxation times also show a clear downward trend as the
temperature increases, which confirms that ![]() ,
, ![]() and
and
![]() are physically
meaningful and can be interpreted as relaxation times
even tough they appear with a non-integer power in equations
(11) and (12).
are physically
meaningful and can be interpreted as relaxation times
even tough they appear with a non-integer power in equations
(11) and (12).
[1287.3.1] The parameters ![]() ,
, ![]() and
and ![]() also
show a temperature dependence.
[1287.3.2] In the case of 5-methyl-2-hexanol (Fig. 4)
there is an increase of
also
show a temperature dependence.
[1287.3.2] In the case of 5-methyl-2-hexanol (Fig. 4)
there is an increase of ![]() with temperature until a plateau
near
with temperature until a plateau
near ![]() is reached.
[1287.3.3] This effect comes from the decreasing slope of the excess wing with
increasing temperature.
[1287.3.4] In the fitting function of model A this behavior can be achieved by
increasing
is reached.
[1287.3.3] This effect comes from the decreasing slope of the excess wing with
increasing temperature.
[1287.3.4] In the fitting function of model A this behavior can be achieved by
increasing ![]() .
[1287.3.5] For the same material there is an apparent increase of
.
[1287.3.5] For the same material there is an apparent increase of ![]() between
between
![]() (
(![]() ) and
) and ![]() (
(![]() )
which has the same origin as the increase in
)
which has the same origin as the increase in ![]() in model A.
[1287.3.6] By increasing
in model A.
[1287.3.6] By increasing ![]() the excess wing becomes less steep.
[1287.3.7] The plateau at
the excess wing becomes less steep.
[1287.3.7] The plateau at ![]() (
(![]() ) and above comes
from the fact that the fits at those
temperatures are done mainly for the
) and above comes
from the fact that the fits at those
temperatures are done mainly for the ![]() -peak,
because the excess wing is not visible.
-peak,
because the excess wing is not visible.
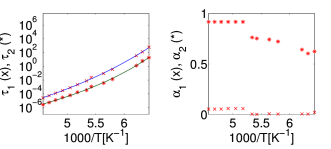
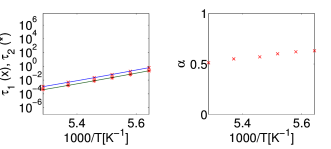
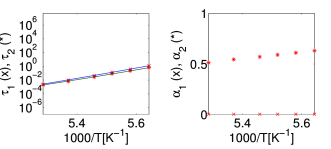
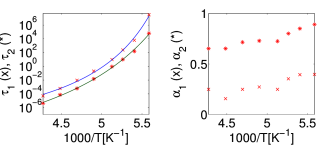
[1287.4.1] For methyl-m-toluate and glycerol there is also a clear temperature dependence
of ![]() ,
, ![]() and
and ![]() (Fig. 5 and Fig. 6).
[1287.4.2] The trend is however reversed in comparison to 5-methyl-2-hexanol.
[1287.4.3] This comes from the increasing slope of the excess wing with
increasing temperature.
[1287.4.4] This behavior can be achieved in the fit functions by decreasing
(Fig. 5 and Fig. 6).
[1287.4.2] The trend is however reversed in comparison to 5-methyl-2-hexanol.
[1287.4.3] This comes from the increasing slope of the excess wing with
increasing temperature.
[1287.4.4] This behavior can be achieved in the fit functions by decreasing ![]() ,
respectively
,
respectively ![]() .
.
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
